Facial Recognition in Airports: Speeding Up Traveler Verification
Categories
Facial Recognition in Airports: Speeding Up Traveler Verification
Airports worldwide are adopting facial recognition for travel to streamline passenger verification, transforming the journey from check-in to boarding into a faster, more secure experience. By automating identity checks, facial recognition when traveling reduces wait times and strengthens security protocols.
However, concerns about privacy and algorithmic fairness remain critical. This article explores how facial recognition for travel operates, its benefits, global implementations, and the challenges shaping its use in the modern world.
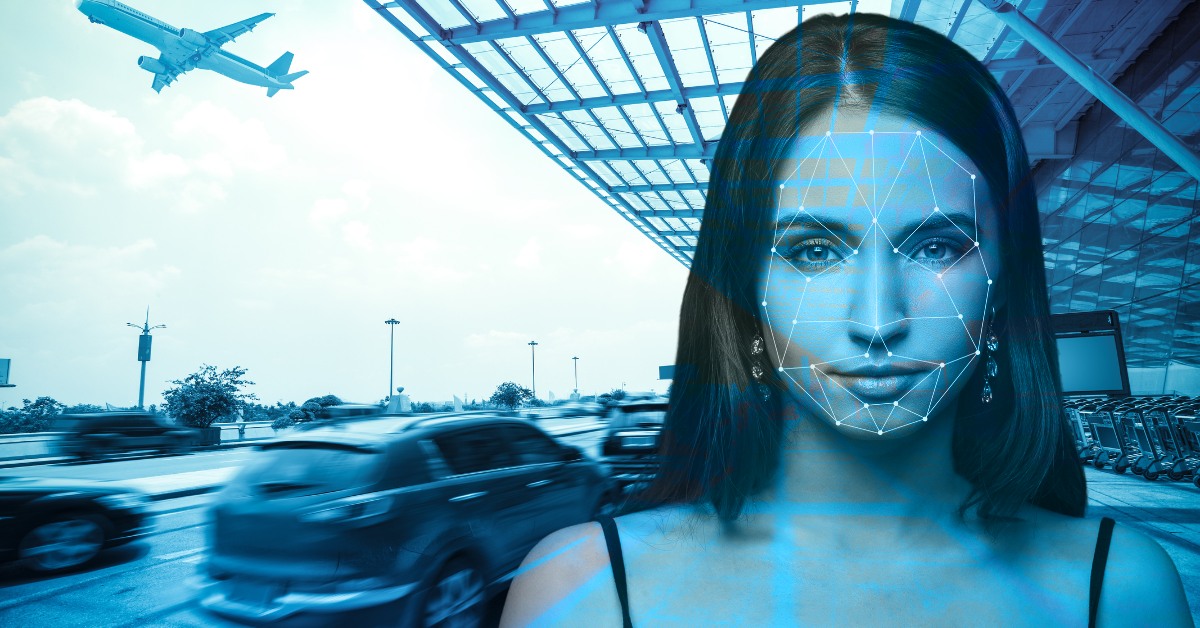

How Facial Recognition Works in Airports
Facial recognition for travel uses biometric technology to verify identities by comparing a traveler’s live facial image to a stored reference, such as a passport or visa photo. At airport kiosks or gates, high-resolution cameras capture a passenger’s face, generating an encrypted facial map. This map is matched against a pre-registered template in a government database within seconds, enabling document-free progression through checkpoints.
For example, at security gates, travelers look into a camera, and the facial recognition technology confirms their identity by matching the live scan to their ID, facilitating a swift, contactless process. This seamless integration enhances efficiency while maintaining robust security standards.
Benefits of Facial Recognition for Travelers
Facial recognition for travel offers significant advantages, improving both airport operations and the passenger experience.
1. Faster Processing
Facial recognition when traveling completes verification in under 6 seconds, significantly reducing delays at check-in, security, and boarding, as reported by major airports in 2024.
2. Improved Security
Automated facial recognition for travel detects fraudulent IDs with high precision, ensuring only authorized passengers proceed, enhancing overall airport safety.
3. Seamless Experience
Travelers can navigate from curb to gate using facial recognition when traveling as their digital ID, eliminating the need to present physical documents multiple times.
4. Scalability
Facial recognition systems for travel efficiently handle large passenger volumes, making them ideal for peak travel seasons at busy international hubs.
Global Adoption of Facial Recognition in Airports
Facial recognition for travel is transforming airport operations globally, with diverse regions leveraging it to optimize verification and security processes.
United States: Widespread Implementation
By 2025, over 120 U.S. airports have implemented facial recognition for travel, led by the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) and U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). At hubs like Dallas-Fort Worth and New York JFK, passengers use facial recognition when traveling for check-in, baggage drop, and international processing, often without physical IDs.
The TSA ensures voluntary participation, with clear opt-out options at checkpoints for those preferring manual verification.
Japan: A Leader in Biometric Travel
Japan leads in facial recognition for travel, with Tokyo’s Narita Airport pioneering the “Face Pass” system since 2022.
Passengers register their face at check-in, enabling document-free navigation through baggage, security, and boarding. This has reduced processing times by 35% for international flights, supporting Japan’s vision for contactless travel.
Narita’s success is driving adoption of facial recognition when traveling across other Asian airports.

Other Regions: Emerging Trends
Facial recognition for travel is gaining traction globally.
In India, Delhi’s Indira Gandhi Airport uses it to expedite domestic passenger flows, cutting security wait times.
In Africa, South Africa’s Cape Town International Airport plans to roll out facial recognition when traveling by 2026, building on pilot programs.
Concerns and Challenges with Facial Recognition
Despite its benefits, facial recognition for travel raises concerns about privacy and fairness. Critics warn of potential data misuse, as some systems retain non-citizen images for extended periods, fueling surveillance fears. Algorithmic bias also persists, with studies indicating higher misidentification rates for individuals with darker skin tones, which could lead to delays or unfair scrutiny.
Additionally, unclear opt-out processes can undermine traveler consent. Airports must implement transparent policies, refined algorithms, and stringent data protections to ensure trust in facial recognition when traveling.
Final Thoughts: Balancing Speed, Security, and Privacy in Travel
Facial recognition for travel is reshaping the airport experience in 2025, delivering unmatched speed, security, and convenience for passengers worldwide. Its widespread adoption, from the U.S.’s major hubs to Japan’s innovative systems, underscores its potential to streamline air travel while enhancing safety. However, challenges like privacy risks, algorithmic bias, and unclear opt-out processes demand proactive solutions.
By investing in equitable algorithms, transparent data policies, and robust security measures, airports can ensure facial recognition when traveling meets the needs of all passengers. As this technology and infrared cameras evolve, it promises to create a future where air travel is not only faster and safer but also inclusive and trustworthy, setting a new standard for global aviation in 2025 and beyond.